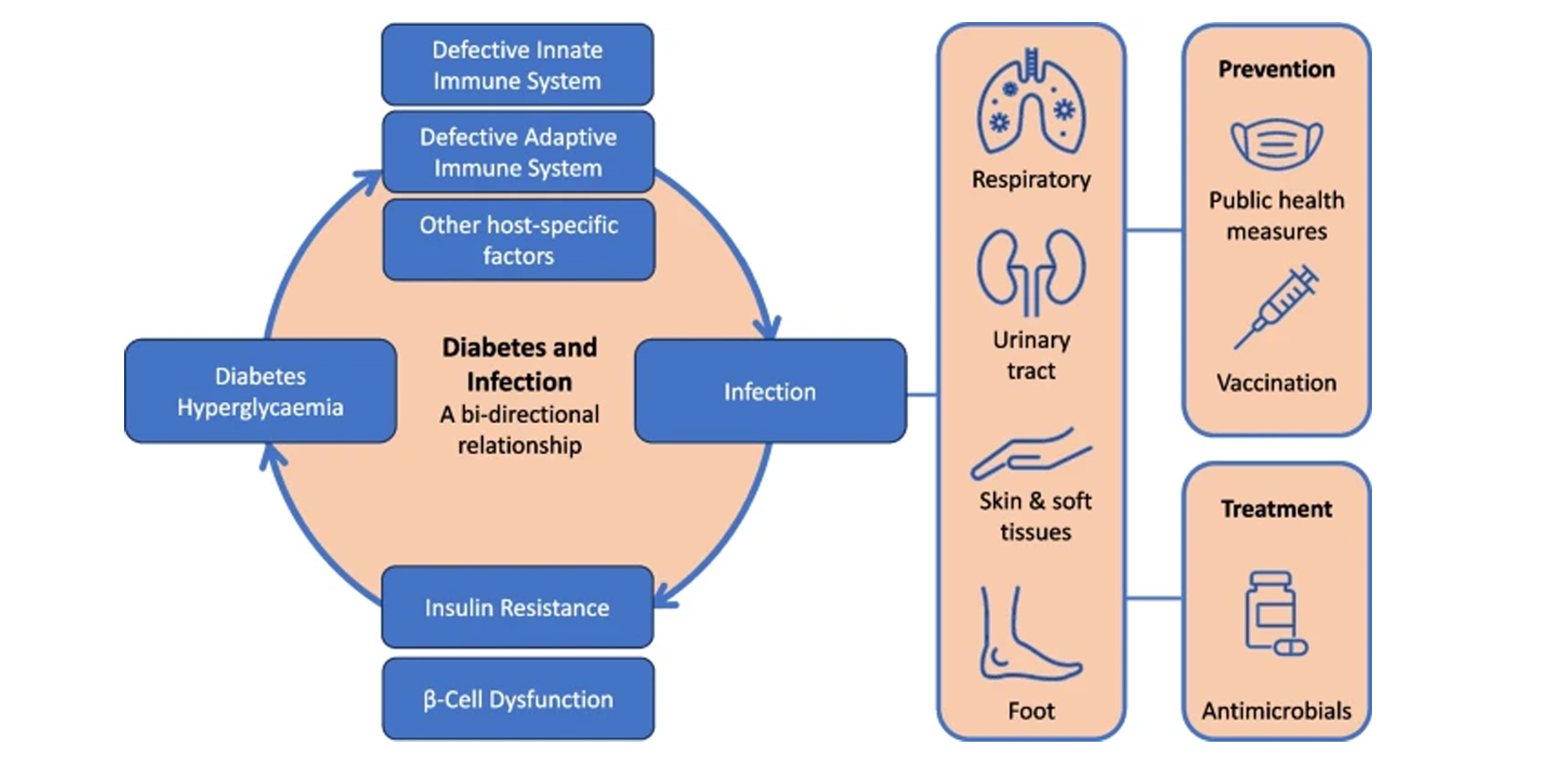
Historically, infections have significantly contributed to morbidity and mortality in individuals with diabetes. While this remains true, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where infections often reveal previously undiagnosed diabetes, the role of infections as a complication of diabetes has not been extensively studied. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing infections compared to the general population, and their infection course tends to be more complex. The COVID-19 pandemic has renewed interest in the intricate relationship between diabetes and infection, especially since individuals with diabetes are more likely to experience severe COVID-19 outcomes and higher mortality rates compared to those without diabetes.
Certain severe infections predominantly affect people with diabetes. Although these infections are relatively rare, they can lead to high mortality if not diagnosed and treated promptly (see Text box). On the other hand, diabetes often complicates more common infections, with the clinical progression influenced by factors such as glycemic control (both recent and long-term), diabetes-related complications, and obesity.
- Infectious Disease Consultations (Diagnosis and management of infections)
- Infusion Services for Intravenous Antibiotics, Remicade, IV Immunoglobulin and Infusion Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis
- Clinical Drug Studies (experimental tests of new antibiotics and treatments)
- Advanced Wound Care including but not limited to Wound VAC, Synthetic Grafts and also available option of Platelet Rich Plasma therapy.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
- Infection Control and Epidemiology
